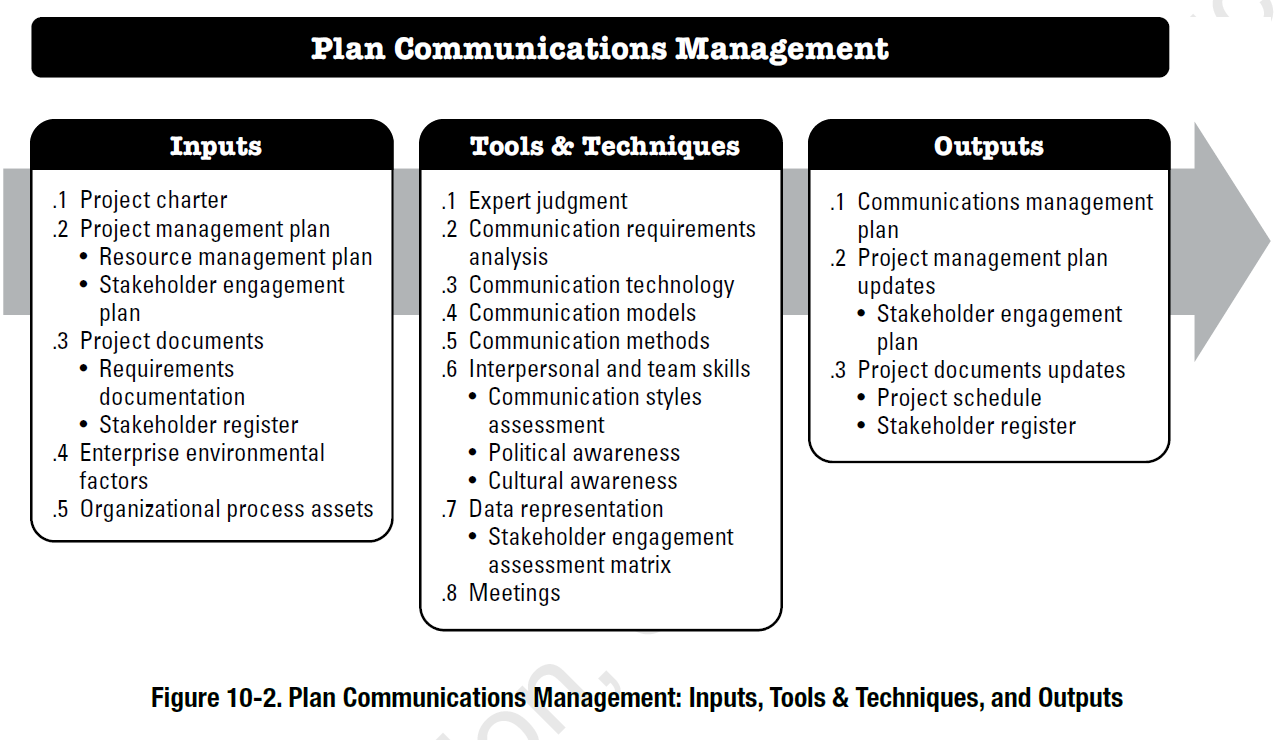
The process of identifying, assessing, and controlling the risks of a business is known as finance risk management. This discipline can be combined with enterprise risk management. It is essential for investors in money markets and the originators structured products. This article will provide more information about finance risk management. Here are three instances where it might be important for your business.
Financial risk management refers to the process of identifying and evaluating potential threats to a company's financial health.
Risk management is an integral part of all business activities, including the purchase U.S. Treasury securities and derivatives used by fund managers. Banks also approve personal lines of credit. Stockbrokers use options and other financial instruments to hedge currency exposure, and money managers use strategies such as asset allocation and portfolio diversification.

The first step of the process is to identify possible risks. These risks may be external or internal to a company. One example is that a technical error or legal liability might cause a financial problem. It could also be due to human error or natural disasters. A successful program for risk management will address all the risks and determine their impact on the organization’s strategic goals.
Investors in the money market need to be aware of this fact
The money market requires investors to have a clear understanding of how to manage risk. This requires a thorough understanding of all types of investments as likewise as the cash flows. A proper risk management strategy will align the supply and demand of funds. Intangible assets are also an important part of a company's risk management strategy.
Many companies are subject to various risks. These risks include credit risks, operational risks, and market risks. Finance firms are more vulnerable than other financial firms to these risks. Financial institutions are more likely to take credit and market risks, while non-financial businesses take operational risks as part of their business.
It is crucial for the originators of structured products
Structured products originators must take a more responsible approach towards risk management in the current market. You can encourage them by requiring them keep a substantial amount of the pool, including the senior and junior tranches. This would give them an incentive to use better risk management and build a more appealing portfolio.
The 2008 financial crisis is an excellent example of why risk management is so important. Many people blame structured finance for the financial crisis, but the crisis was caused by poor risk management. Problems were not caused by the products; rather, they were due to the poor risk management of many financial institutions such as banks and mortgage brokers.
FAQ
It can sometimes seem difficult to make business decisions.
Complex systems with many moving parts are the hallmark of businesses. It is difficult for people in charge of businesses to manage multiple priorities simultaneously and also deal with uncertainty.
It is important to understand the effects of these factors on the system in order to make informed decisions.
To do this, you must think carefully about what each part of the system does and why. It is important to then consider how the individual pieces relate to each other.
Ask yourself if there are hidden assumptions that have influenced your behavior. If not, you might want to revisit them.
You can always ask someone for help if you still have questions after all of this. You might find their perspective is different from yours and they may have insight that can help you find the solution.
How does a manager learn to manage?
By practicing good management skills at all times.
Managers must continuously monitor the performance levels of their subordinates.
You should immediately take action if you see that your subordinate is not performing as well as you would like.
You should be able to identify what needs improvement and how to improve things.
What role can a manager fill in a company’s management?
Each industry has a different role for a manager.
The manager oversees the day-to-day activities of a company.
He/she makes sure that the company meets its financial obligations, and that it produces goods or services that customers desire.
He/she ensures employees adhere to all regulations and quality standards.
He/she plans new products and services and oversees marketing campaigns.
Statistics
- This field is expected to grow about 7% by 2028, a bit faster than the national average for job growth. (wgu.edu)
- Hire the top business lawyers and save up to 60% on legal fees (upcounsel.com)
- UpCounsel accepts only the top 5 percent of lawyers on its site. (upcounsel.com)
- As of 2020, personal bankers or tellers make an average of $32,620 per year, according to the BLS. (wgu.edu)
- The average salary for financial advisors in 2021 is around $60,000 per year, with the top 10% of the profession making more than $111,000 per year. (wgu.edu)
External Links
How To
How can you implement Quality Management Plan (QMP).
QMP (Quality Management Plan) is a system to improve products and services by implementing continuous improvement. It focuses on the ability to measure, analyze and control processes and customer satisfaction.
QMP is a standard way to improve business performance. QMP improves production, service delivery, as well as customer relations. QMPs must include all three elements - Products, Services, and Processes. If the QMP only covers one aspect, it's called a "Process QMP". When the QMP focuses on a Product/Service, it is known as a "Product" QMP. If the QMP focuses on Customer Relationships, it's called a "Product" QMP.
When implementing a QMP, there are two main elements: Scope and Strategy. They can be described as follows:
Scope is what the QMP covers and how long it will last. For example, if you want to implement a QMP that lasts six months, then this scope will outline the activities done during the first six.
Strategy: This describes the steps taken towards achieving the goals set forth in the scope.
A typical QMP has five phases: Planning (Design, Development), Implementation (Implementation), and Maintenance. The following describes each phase.
Planning: This stage identifies and prioritizes the QMP's objectives. All stakeholders involved in the project are consulted to understand their requirements and expectations. Next, you will need to identify the objectives and priorities. The strategy for achieving them is developed.
Design: The design stage involves the development of vision, mission strategies, tactics, and strategies that will allow for successful implementation. These strategies are then put into practice by creating detailed plans.
Development: The development team is responsible for building the resources and capabilities necessary to implement the QMP effectively.
Implementation is the actual implementation of QMP according to the plans.
Maintenance: Maintaining the QMP over time is an ongoing effort.
Additionally, the QMP should include additional items:
Stakeholder involvement is important for the QMP's success. They must be involved in all phases of the QMP's development, planning, execution, maintenance, and design.
Project Initiation: The initiation of any project requires a clear understanding of the problem statement and the solution. Also, the initiator should understand why they are doing it and what they expect.
Time Frame: The time frame of the QMP is very critical. The simplest version can be used if the QMP is only being implemented for a short time. You may need to upgrade if you plan on implementing the QMP for a long time.
Cost Estimation: Cost estimation is another vital component of the QMP. It is impossible to plan without knowing what you will spend. Cost estimation is crucial before you begin the QMP.
The most important thing about a QMP is that it is not just a document but also a living document. It evolves as the company grows and changes. So, it should be reviewed periodically to make sure that it still meets the needs of the organization.